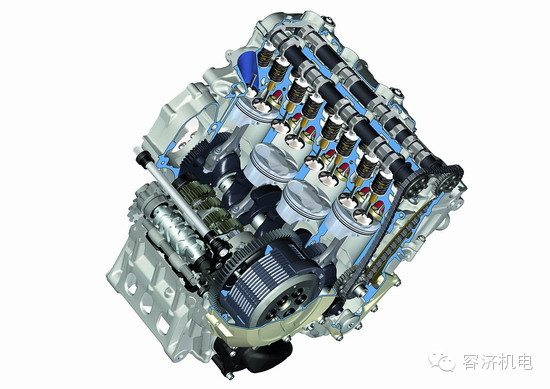
The engine is a complex system composed of multiple parts, each playing a crucial role in its overall performance. One of the most important components is the cylinder head, which sits at the top of the engine and houses the intake and exhaust valves. These valves are responsible for allowing air and fuel into the combustion chamber and expelling the spent gases after combustion. The number of valves can vary depending on the design—common configurations include two-valve and four-valve setups. More valves generally mean better airflow, leading to improved engine efficiency and higher performance, especially at high speeds.

Inside the cylinder head, you’ll find the intake and exhaust valves. Typically, the larger valve is for intake, while the smaller one handles exhaust. The more valves an engine has, the better it can breathe, resulting in more power and smoother operation. This is why modern engines often use four or even five valves per cylinder. However, the design must balance complexity with reliability, as too many valves can increase maintenance and cost.
The cylinder itself is where the combustion process takes place. It’s a hollow space that holds the piston, which moves up and down during the engine's cycle. When the air-fuel mixture ignites, it creates pressure that pushes the piston downward, turning the crankshaft and generating power. The size of the cylinder directly affects the engine's displacement, measured in cubic centimeters (cc), and thus influences its power output.
The gearbox, or transmission, plays a vital role in transferring power from the engine to the wheels. It allows the vehicle to shift gears, adjusting the ratio between engine speed and wheel speed. This makes it possible to achieve both high torque for acceleration and high-speed cruising. Gearboxes are typically heavy and complex, making them one of the heaviest components in the engine system.
Engines can be classified based on their stroke cycles: two-stroke and four-stroke. A two-stroke engine completes a power cycle in just two strokes of the piston, while a four-stroke engine requires four. Although two-stroke engines produce more power relative to their size, they are less efficient and emit more pollutants. This is why many countries have restricted their use, especially in new vehicles. Despite this, two-stroke engines are still used in some specialized applications due to their simplicity and high-revving capabilities.
Cooling systems are essential for maintaining optimal engine temperatures. Water-cooled engines use coolant to absorb heat from the engine block and transfer it to a radiator, where it is dissipated by airflow. Air-cooled engines rely on fins and natural airflow to cool the engine, making them simpler but less effective at high temperatures. Oil-cooled engines use engine oil to help regulate temperature, though they still require additional cooling methods for the cylinder and head.
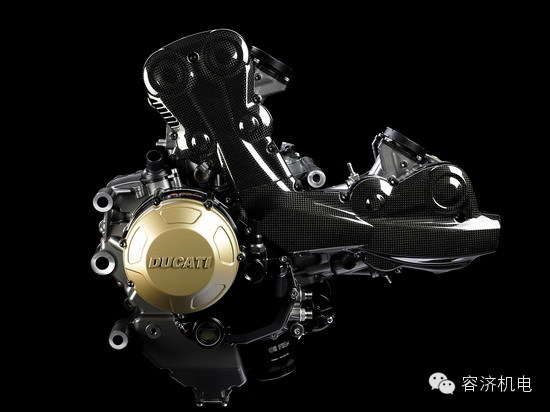
Single-cylinder engines are the simplest type, featuring one piston and cylinder. They are commonly used in small vehicles, generators, and lawn mowers due to their low cost and ease of maintenance. However, they tend to vibrate more and are not ideal for high-speed performance. Twin-cylinder engines offer better balance and smoother operation, making them popular in motorcycles and scooters. Three-cylinder and four-cylinder engines provide even greater power and refinement, with four-cylinder engines being the most common in modern cars and motorcycles.
Each engine type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the intended use, performance requirements, and environmental considerations. Whether it’s a single-cylinder for simplicity, a twin-cylinder for balance, or a four-cylinder for power, understanding these differences helps in selecting the right engine for the job.
Galvanized Wire: Galvanized wire refers to a type of wire that has been coated with a layer of zinc to enhance its corrosion resistance. The process of galvanization involves immersing the wire in a bath of molten zinc or applying a zinc coating through electroplating. Galvanized wire is commonly made from carbon steel wire and is used in a wide range of applications, including fencing, construction, agriculture, and crafts. The zinc coating provides protection against rust and extends the lifespan of the wire.
Galvanized Steel Wire Netting: Galvanized steel wire netting, also known as galvanized WIRE MESH, is a type of wire mesh that is made from galvanized steel wires. The wires are woven or welded together to form a grid pattern, creating a strong and durable mesh structure. Galvanized steel wire netting is commonly used for various applications, including fencing, animal enclosures, garden protection, and filtration. The galvanized coating provides excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for outdoor and harsh environments.
Galvanized Binding Wire: Galvanized binding wire is a type of wire that is specifically designed for binding and tying applications. It is made from galvanized steel wire and is commonly used in construction, packaging, and other industries. Galvanized binding wire provides strength and durability for securing and fastening materials together. The galvanized coating adds corrosion resistance, ensuring the wire remains intact and reliable over time.
Galvanized Steel Wire: Galvanized steel wire refers to a type of steel wire that has undergone the galvanizing process. It is made from carbon steel wire that has been coated with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. Galvanized steel wire is widely used in various applications, including fencing, construction, electrical wiring, and manufacturing. The galvanized coating provides excellent rust resistance, making the wire suitable for both indoor and outdoor environments.
These different types of galvanized wires, including galvanized wire, galvanized steel wire netting, galvanized binding wire, and galvanized steel wire, offer enhanced corrosion resistance and durability. The specific choice depends on the intended application, required strength, and environmental conditions.
Galvanized Wire,Galvanized Steel Wire Netting,Galvanized Binding Wire,Galvanized Steel Wire
Hebei Aibuer trading co., Ltd , https://www.ablehardwares.com
