Recently, the Biomass High Efficiency Conversion Research Group (1816 Group) led by Professor Zhao Zongbao of the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, for the first time realized glucose and xylose production of oils and fats in the study of biomass energy. This important research result was recently published in Biotechnology for Biofuels (Hu et al., Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2011, 4: 25).
Biomass is mainly composed of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. Its hydrolysis product has the basic characteristics of coexistence of glucose and xylose. One of the common problems in the conversion of biomass hydrolysate into liquid fuels is the fact that raw materials containing glucose and xylose cannot be used efficiently by microorganisms. Biodiesel is an important liquid biofuel. Its bottleneck for large-scale application is insufficient supply of raw materials for oils and fats. Microbial lipids have a fatty acid composition similar to that of animal and vegetable fats and can be used in the preparation of biodiesel.
The Dalian Institute of High-Efficiency Biomass Conversion Research Group has devoted many years to research on converting biomass into biodiesel. Through screening, it was found that some oleaginous yeasts can use glucose and xylose simultaneously to accumulate lipids in the cells, and the lipid content of the bacteria reached 59%. The oleaginous yeast was directly cultured with corn straw hydrolysate, and the bacterial oil and fat content reached 39%.
The research results are of great significance to the development of mixed sugar simultaneous bio-transformation technology, reduction of microbial oil production raw material costs, and expansion of biodiesel industry raw materials.
Trichoderma spp.
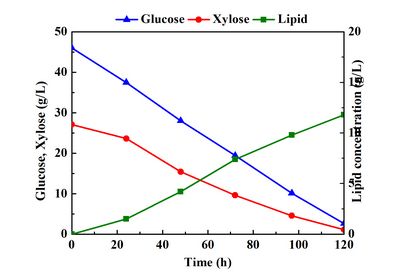
Synthetic conversion of glucose and xylose to produce oil
Qingdao Friend New Energy Development CO.,LTD , http://www.friendtyres.com
