Liu Mingyao
Huangshan, April 2013

1 Standardization of basic concepts
1.1 standard standard
A normative document that is developed by consensus and approved by a recognized body for the best order within a certain scope.
Note 1: Based on the combined results of science, technology and experience, the aim is to promote the best mutual benefits.
Note 2: Consensus does not mean that there is no objection, but rather that, once a vote is required, usually three-quarters (China) or two-thirds (ISO, IEC) consent is used as a sign of consensus. [Quoted from GB/T 20000.1-2002, definition 2.3.2], this definition is also the definition of standards by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
1.2 standardized standardization
In order to obtain the best order within a certain range, the activities of the terms of common use and reuse are formulated for practical or potential problems.
Note 1: Includes the process of preparing, publishing and implementing standards.
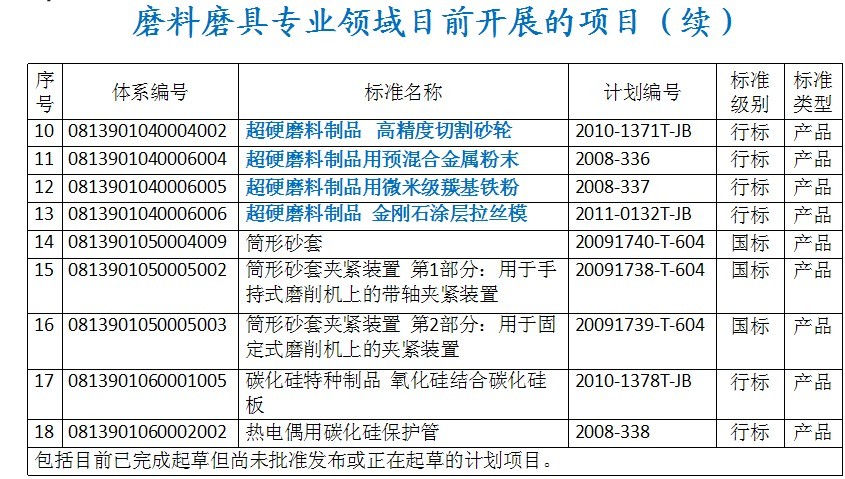
Note 2: The main role is to improve the applicability of products, processes or services, prevent trade barriers and promote technical cooperation. [quoted from GB/T 20000.1-2002, definition 2.1.1]
2. Strategic significance of standardization
2.1 The role and significance of the standard
Necessary conditions for modern large-scale production The basis of scientific management The need to adjust product structure and industrial structure The necessary means to expand the market Promote the transformation of science and technology into a platform for productivity Promote the bridge and link of trade development Improve quality and protect safety
(1) Necessary conditions for modern large-scale production: Standards can regulate social production activities, regulate market behavior, lead economic and social development, promote the establishment of optimal order, and promote the mutual coordination and cooperation of related products in technology. With the development of science and technology, the degree of socialization of production is getting higher and higher, the technical requirements are more and more complex, and the production cooperation is more and more extensive. Many industrial products and engineering constructions often involve dozens, hundreds, or even tens of thousands of companies, with collaboration points all over the world. Such a complex production mix objectively requires that the production activities must be technically highly uniform and coordinated. This must be through the development and implementation of a large number of technical standards, work standards and management standards, so that the production departments and the production processes within the enterprise are organically linked to ensure that production is carried out in an orderly manner.
(2) The foundation of scientific management: Standards are conducive to achieving scientific management and improving management efficiency. Modern production is about efficiency, and efficiency is the benefit. Modern enterprises implement automation and computerized management, and the premise is standardization.
(3) The need to adjust the product structure and industrial structure: Standards can make rational use of resources, simplify production technology, realize interchangeable combination, and create conditions for adjusting product structure and industrial structure.
(4) The necessary means to expand the market: the purpose of production is to consume, and the producer must find the consumer to develop the market. The standard not only provides the possibility of expanding production scale and meeting market demand, but also creates conditions for implementing after-sales service and expanding competition. It should be emphasized that due to the increasing socialization of production, the economic development of various countries and regions has been closely integrated with the global economy. Standards and standardization have not only opened the way for a world-integrated market, but also entered Such a market sets a threshold.
(5) Promoting the transformation of science and technology into a platform for productivity: Science and technology are the primary productive forces, but before science and technology go out of the laboratory, it only affects and functions in the field of science and technology. It is potential productivity, not actual productivity. . Only through the unified platform provided by technical standards can science and technology be quickly and quickly transitioned to the production field, and the actual productivity will be transformed, thus generating the economic and social benefits. Standards and technology advancement have a very close relationship, and the two complement each other and promote each other. Standards are an important “bridge†for the transformation of scientific and technological achievements into productive forces. Advanced scientific and technological achievements can be transformed into productive forces and promote social progress through standardized means.
(6) Bridges and ties to promote trade development: Standards can enhance mutual communication and understanding among countries in the world, eliminate technical barriers, and promote international economic and trade development and scientific, technological and cultural exchanges and cooperation. The current world has been integrated into highly developed information and trade. The trend of globalization of trade and market integration is unstoppable, and the bridges and ties that can truly play a role in various countries and regions are technical standards. Only when the world organizes production and trade according to the same standard, can market behavior play its due role in a larger scope and in a broader field, and the material wealth and spiritual wealth created by human beings can be shared by human beings all over the world. .
(7) Improve quality and protect safety: Standards are conducive to stabilizing and improving the quality of products, engineering and services, promoting enterprises to take the road of quality and efficiency development, enhancing the quality of enterprises, improving the competitiveness of enterprises; protecting human health and ensuring personal and property safety. Protect the human ecological environment, make rational use of resources, and safeguard consumer rights. The technical standard is the main basis for measuring the quality of a product. It not only specifies the product performance, but also clearly defines the product specifications, inspection methods, packaging, storage and transportation conditions. Strictly produced according to standards, inspection, packaging, transportation and storage according to standards, product quality can be guaranteed. The standard level marks the level of product quality. Without a high standard, there is no high quality product.
2.2 Background from the standardization strategy
2.2.1 The need for economic globalization
With the development of economic globalization and regional integration, economic exchanges and technological exchanges have broken the original boundaries and formed large-scale production and large circulation on a global scale.
How to ensure the healthy and orderly development of the global economic market (the best order on a global scale), the World Trade Organization (WTO) through the signing of the Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (WTO/TBT Agreement) and the implementation of sanitary and phytosanitary measures The Agreement (WTO/SPS Agreement) and other methods use the standard as the language of economic globalization communication.
Standards can be used as a catalyst for promoting international economic exchanges and as a tool for artificially setting up trade barriers. The wave of globalization economic development has pushed standardization to a strategic position.
2.2.2 The need for economic globalization competition
Economic globalization has increased the degree of interdependence among countries in the world, but it has also intensified competition among countries.
While the World Trade Organization regards standards as the language of economic globalization, it also raises the standard to the status of international trade rules.
"Three-stream enterprises sell coolies, second-rate enterprises sell products, first-class enterprises sell patents, and super-class enterprises sell standards." It reveals the "rules of the game" that "the standard is the best in the world". Whoever masters the standard can build a "benefit for itself" The rules of the game, not only got the pass, but also mastered the right to speak.
2.3 Significance of implementing a standardization strategy
1. The important foundation of science and technology, economic and social development 2. The important technical means to regulate the order of the market economy 3. The central link of adjusting the industrial structure and transforming the economic growth mode 4. Solving the low level of product standards, the poor awareness of corporate standards, and the technical content of brands Important measures with less market competitiveness and weaker competition 5. More competitive forms than products and brands, higher levels, and more influential forms of competition 6. Basic guarantees for global trade 7. Inevitable measures to deal with foreign technical barriers to trade 8. Improve the country And the basic elements of the company's core competitiveness and soft power 9. Implementing the standardization strategy is of great strategic significance for accelerating economic and social development, promoting industrial structure optimization, promoting independent innovation, actively responding to foreign technical barriers to trade, and building economic core competitiveness.
2.4 Standardization strategies of major developed countries (regional alliances)
The ultimate goal: to maximize the economic interests of the country, to compete and lead international standards as the preferred strategy for international economic competition, to compete for the drafting rights, participation rights and leadership of international standards in relevant international institutions, the degree of fierceness compared with the competition in the commodity market Favorably.
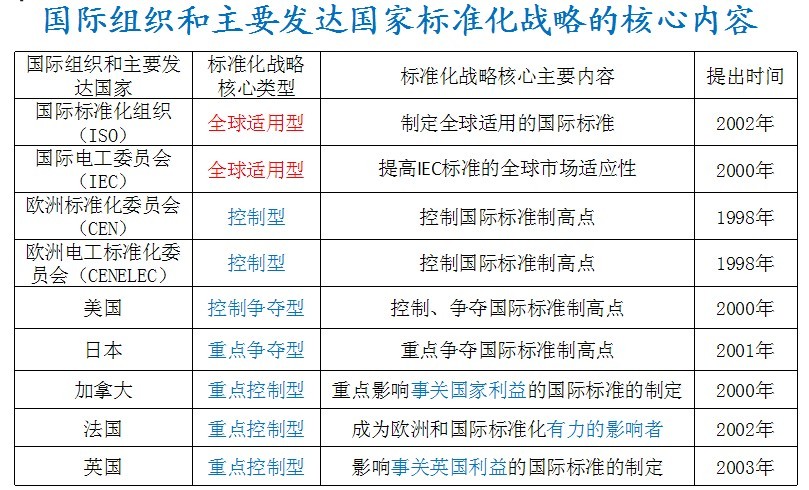
2.5 China's standardization strategy
2.5.1 Objectives of China's standardization strategy
From the low end of the global production value chain (only responsible for processing and manufacturing, assembly, etc.) to the high-end (with product development, brand, core technology, standards, etc.), take the initiative in global competition.
Encourage innovation, master core technologies, organically combine core technologies, intellectual property rights, and standards, give full play to the combined effects, focus on formulating standards with independent intellectual property rights, and achieve leap-forward development of industry and economy.
Strive to make China's technical standards' international competitiveness and substantive participation in international standardization activities by 2020, meet the needs of national science and technology, trade and industrial development strategies, and strongly support China's trade powers to become trade powers and safeguard national economic interests.
Strategic significance of standardization work
2.5.2 The core of China's standardization strategy
(1) Improve the adaptability of standards
Improve the ability of standards to meet the needs of technology, trade and industrial development.
(2) Improve the competitiveness of standards
Improve the ability of standards in market competition, especially in international market competition.
2.5.3 Tasks of China's standardization strategy
(1) Promote the rapid transformation of scientific and technological research and development results into standards, improve the content of independent innovation technologies in standards (2) Effectively adopt international standards, improve the efficiency and effectiveness of adopting international standards (3) Actively and focusly participate in the formulation of international standards, and promote China's technical standards have become international standards.
China's standardized management system
1 Basic situation
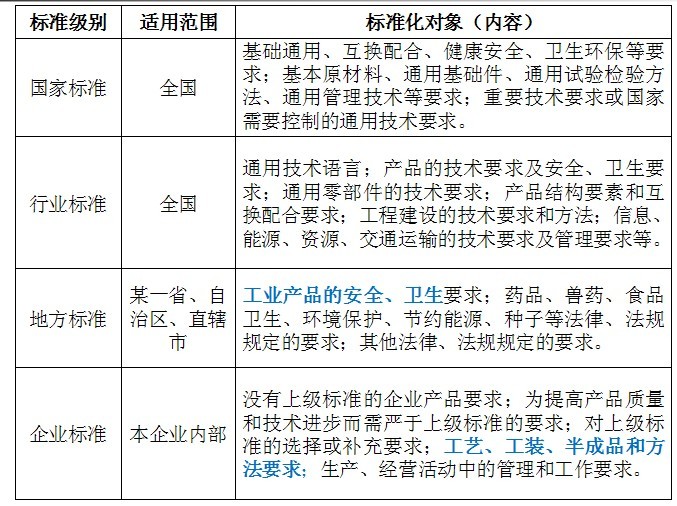
According to the current "Standardization Law of the People's Republic of China", the standard system is divided into four levels: national standards, industry standards, local standards and enterprise standards.
National standards require uniform technical requirements across the country. Formulated by the competent department of standardization administration under the State Council.
Industry standards do not have national standards and require uniform technical requirements within a certain industry across the country. It shall be formulated by the relevant administrative department of the State Council.
Local standards do not have national standards and industry standards, but also require the safety and hygiene requirements of industrial products that are unified within the provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the Central Government. It shall be formulated by the administrative department of standardization of provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government.
If the products produced by enterprise standard enterprises do not have national standards and industry standards, they shall be formulated as the basis for organizing production. It must be reported to the local government standardization administrative department and the relevant administrative department for the record.
National, industry, and local standards are divided into mandatory standards and recommended standards.
Mandatory standards - standards for the protection of human health, personal and property safety, and standards enforced by laws and administrative regulations - must be implemented, products that do not meet mandatory standards, and production, sales and imports are prohibited.
The recommended standards countries encourage enterprises to adopt voluntarily, but once adopted, they are binding on the adoption of enterprises. If they are not adopted, enterprise product standards that are stricter than national standards or industry standards should be formulated.
The state encourages the active adoption of international standards.
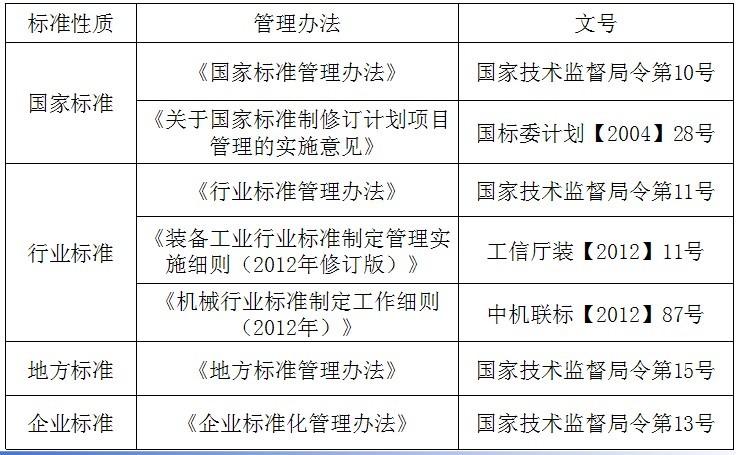
2 Laws and regulations
2.1 Standardization Law and its Implementation Regulations
The Standardization Law of the People's Republic of China (Decree No. 11 of the President of the People's Republic of China on December 29, 1988) regulates the formulation, implementation, and legal responsibilities of standards, and is the basic legal basis for China's standardization work;
The Regulations for the Implementation of the Standardization Law of the People's Republic of China (Order No. 53 of the State Council of the People's Republic of China on April 6, 1990) made specific provisions on the management of standardization work, the formulation, implementation and supervision of standards, and legal responsibilities. Carry out specific requirements for standardization work.
2.2 Standard management methods at all levels
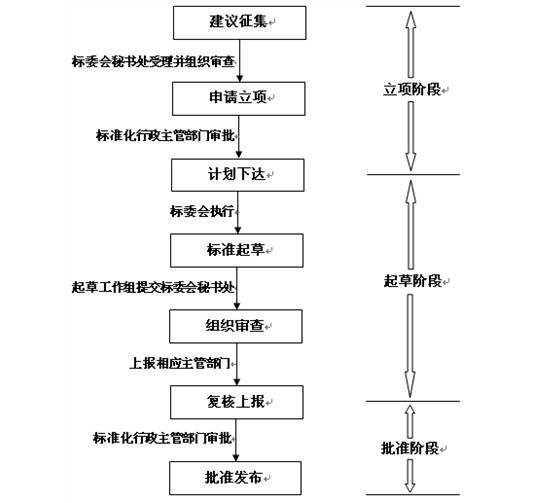
3. Standard setting procedure
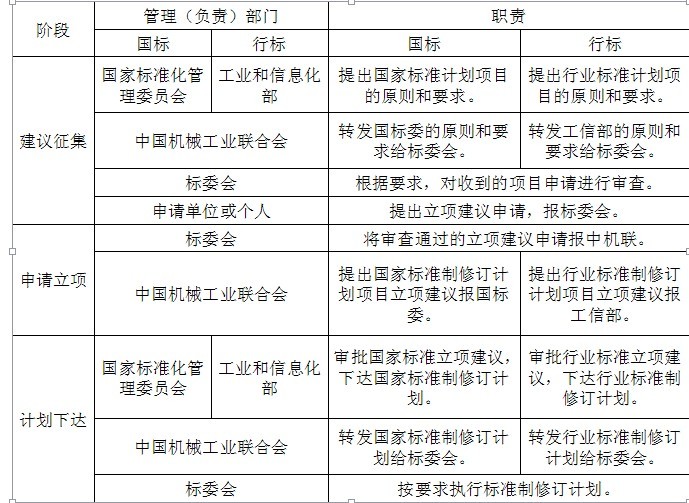
4. Standards management (responsible) departments and their duties at various stages
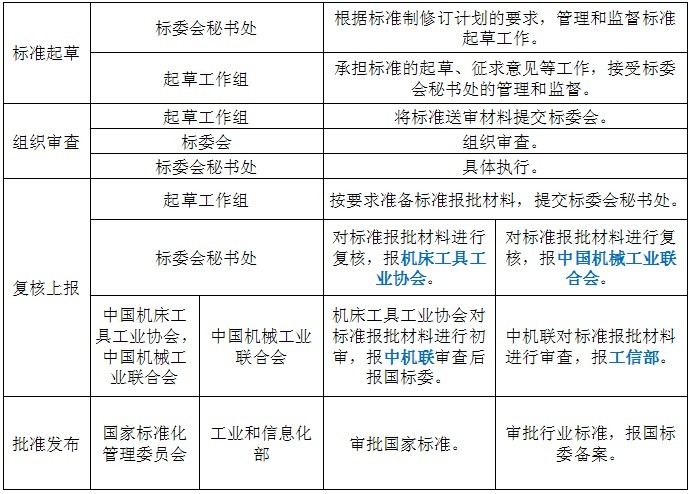
5 Principles and requirements for setting standards
5.1 General principles and requirements
Develop a socialist commodity economy, promote technological progress, improve product quality, improve social and economic benefits, safeguard the interests of the country and the people, and adapt the standardization work to the needs of socialist modernization and the development of foreign economic relations.
Encourage the adoption of international standards and advanced foreign standards and actively participate in the development of international standards.
For the following technical requirements that require uniformity, standards should be established:
(1) The variety, specification, quality, grade or safety and sanitary requirements of industrial products;
(2) Safety, hygiene requirements for the design, production, testing, inspection, packaging, storage, transportation, use of industrial products or production, storage and transportation;
(3) Various technical requirements and test methods related to environmental protection;
(4) Technical terms, symbols, code numbers, drawing methods, and interchange coordination requirements for industrial production, engineering construction and environmental protection (5) Agricultural (including forestry, animal husbandry, fishery, the same below) products (including seeds and seedlings) , breeds, breeders, the same as the varieties, specifications, quality, grade, inspection, packaging, storage, transportation and production technology, management technology requirements;
(6) Technical requirements for information, energy, resources and transportation.
5.2 Principles and requirements for standards at all levels
5.2.1 National standards
The relevant national guidelines, policies, laws and regulations should be implemented to facilitate the rational development and utilization of national resources, promote scientific and technological achievements, actively adopt international standards and advanced foreign standards, and promote the development of foreign economic and technological cooperation and foreign trade to ensure safety and the people's body. Health, environmental protection, fully consider the use requirements, and protect the interests of consumers with advanced technology, reasonable economics, safety, reliability, and coordination.
5.2.2 Industry Standards
It shall not be inconsistent with the relevant national standards. The relevant industry standards shall be coordinated and unified. The industry standards shall not be repeated. After the implementation of the corresponding national standards, the machinery industry standards shall be abolished. “Marketing, service industry, self-determination, timely introduction, timely revision "Continuous improvement" principle combined with technological innovation, test verification, industrial promotion, application promotion, and overall promotion
5.2.3 Local standards
Abolished after the implementation of the corresponding national standards or industry standards
5.2.4 Enterprise Standard
The state encourages companies to set corporate standards that are stricter than national or industry standards and are applicable within the enterprise.
Record the filing within 30 days after the release.
According to the affiliation of the enterprise, it shall be reported to the local government standardization administrative department and the relevant administrative department for the record.
After the standard review, the results of the review shall be reported to the acceptance and filing department in a timely manner.
Revise the standard and re-record it.
The specific filing method shall be handled in accordance with the regulations of the people's governments of provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government.
5.3 Main differences between standards at all levels
1 National Abrasives Standardization Technical Committee
SAC/TC 139
Established in 1988 by the former State Bureau of Technical Supervision;
Technical organization engaged in national standardization work in the field of abrasives and abrasives;
Standardized technology in the field of abrasives and abrasives;
The secretariat is located in Zhengzhou Abrasives Grinding Research Institute.
Standardization of the field of abrasives
The National Abrasives Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC 139) was established in 1988 by the former State Bureau of Technical Supervision. The technical organization of the national standardization work in the field of abrasives and abrasives, and the standardization of technical expertise in the field of abrasives and abrasives. Work, under ordinary abrasive (TC 139/SC 1), ordinary abrasive and Silicon Carbide special products (TC 139/SC 2), super-hard abrasives and products (TC 139/SC 3), coated abrasives (TC 139) /SC 4) Four subcommittees. The secretariat is located in Zhengzhou Abrasives Grinding Research Institute.
Four subcommittees
Ordinary abrasive (TC 139/SC 1)
Ordinary Abrasives and Silicon Carbide Special Products (TC 139/SC 2)
Superabrasives and products (TC 139/SC 3)
Coated Abrasives (TC 139/SC 4)
Member staff
Production, use, distribution, scientific research institutions, testing institutions, universities, industry associations and government departments.
Production of members
Application by the relevant unit The Secretariat makes recommendations. The competent authority recommends the National Standardization Management Committee to be appointed for a term of five years.
The Standards Committee consists of representatives from enterprises, scientific research institutions, testing institutions, universities, industry associations, government departments, etc. from production, use and distribution. The members of the standard committee shall apply by the relevant units, the secretariat of the standard committee shall make recommendations, and the competent authorities shall recommend them to be appointed by the National Standardization Administration Committee for a term of five years. There were 102 members of the 5th Standardization Committee and 143 members were appointed.
2. Relevant management system
2.1 Standard Committee Management
The "National Abrasives Standardization Technical Committee Charter" stipulates the tasks, organization, work procedures, committee members' rights and obligations, and fund management of the National Abrasives Standardization Technical Committee.
2.2 Secretariat management
The Working Rules of the Secretariat of the National Abrasives Standardization Technical Committee stipulates the tasks, working systems and fund management of the Secretariat of the National Abrasives Standardization Technical Committee.
2.3 Standard Project Management
The "National Abrasives Standardization Technical Committee Standards and Revisions Project Management Measures" stipulates the principles of the standard revision and revision project management in the field of abrasives and abrasives, the standard establishment procedures, the drafting procedures for drafting units and drafters, the drafting and review of standards, Standard approval and rewards and punishments.
The “National Abrasives Standardization Technical Committee Standard Revision Plan Project Implementation Proposal (Trial)†stipulates the general principles of the proposal for the establishment of the standard revision and revision project of the abrasives and abrasives, the proposal of the project proposal, and the review and project approval of the project proposal. Suggested reviews and so on.
3. Basic situation of the standard system in the field of abrasives
In order to implement the "Equipment Manufacturing Industry Adjustment and Revitalization Plan", in July 2010, the National Abrasives Standardization Technical Committee was entrusted by the National Standardization Management Committee Industry Standards Department to undertake the "Research on Abrasives Standard System".
Based on the development status of the abrasives industry, the research team carried out the research on the standard system of abrasive abrasives and the development of important standards, and proposed the structure and layout of the standard system of abrasives.
3.1 Abrasives field standard system
In October 2012, in accordance with the requirements of the "French Secrets [2012] No. 168 "Notice on the construction of the 12th Five-Year" technical standard system for the machinery industry, in order to better support the industrial transformation and upgrading, accelerate the establishment of adaptation The technical standard system for the development of the machinery industry, the National Abrasives Standardization Technical Committee has compiled the "Twelfth Five-Year" technical standard system construction program of the machinery industry - the field of abrasives and abrasives.
Based on the existing achievements of the research on the standard system of abrasives and abrasives, the scheme has improved and optimized the standard system based on the analysis of the status quo and trends of technology and industry development.
System framework
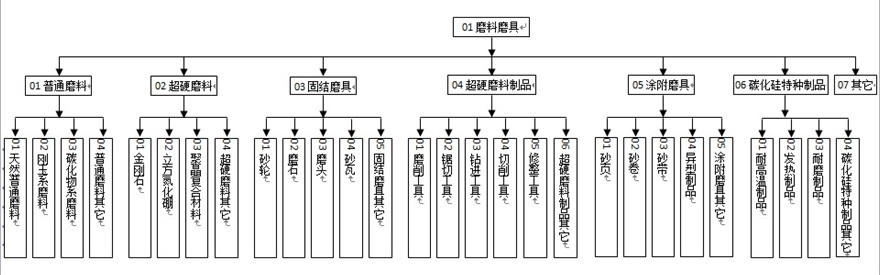
From the birth of the first abrasive tooling standard in China in 1959, the standard system covering six major categories of abrasives in the abrasives industry has been formed.
Through independent research and development and the adoption of international and foreign advanced standards, a relatively complete and coordinated standard system has been formed, which provides important technical support for the development of the entire industry, and can basically meet the needs of the industry and the market.
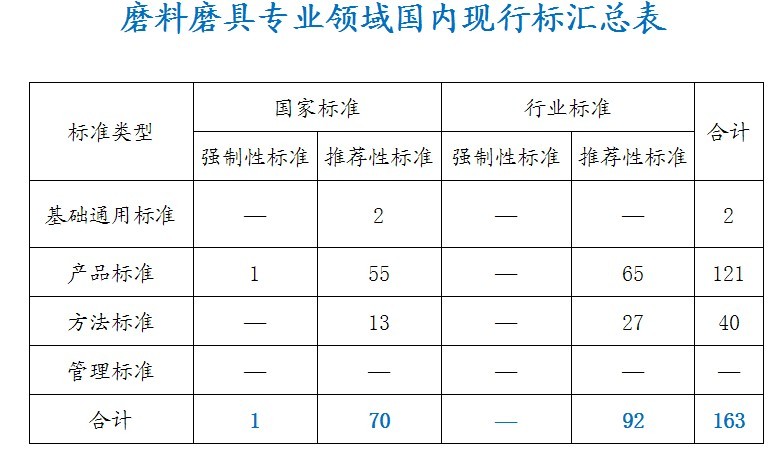
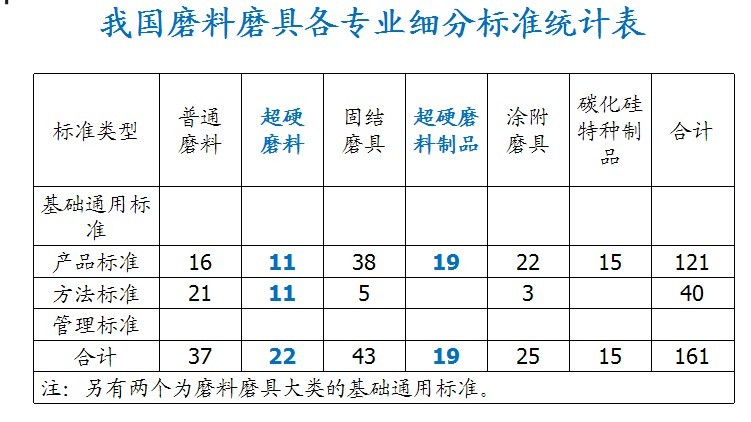
3.2 Status of standards in abrasive abrasives
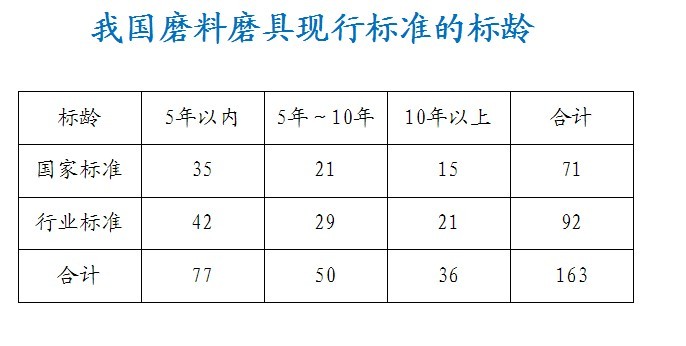
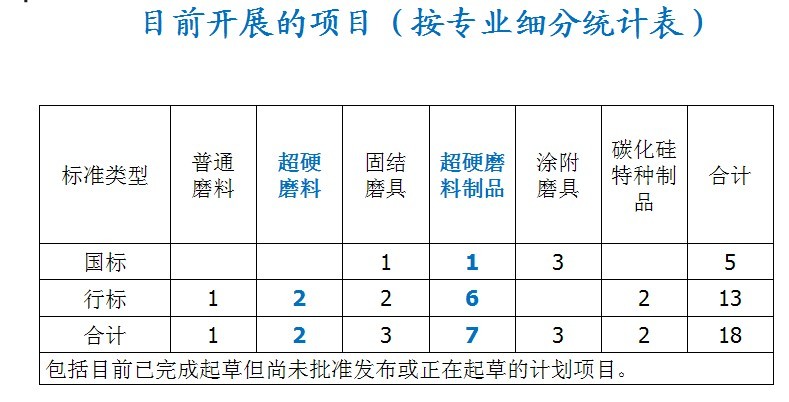
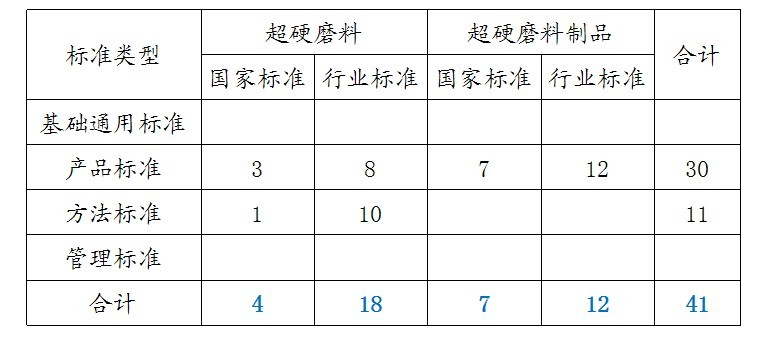
There are 163 items, 71 national standards and 92 industry standards.
It constitutes the basic general, products, and methods; one mandatory and 162 recommended.
The applicability is comprehensive, basically meeting the needs of relevant aspects such as production technology, product quality inspection, quality supervision and management, marketing, etc., and the applicability is good.
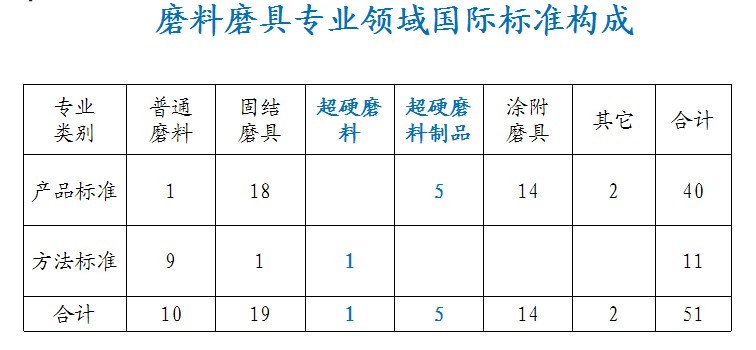
51 international standards were adopted, 43 were transformed, 8 were not adopted because the international standards could not meet the market demand or the domestic experimental conditions were immature. The adoption rate was 84.3%, and the overall standard was better. Foreign advanced standards are used as reference for technical data and are not directly adopted.
Standard timeliness Most standards have a standard age of less than 10 years, of which 77 are within 5 years and 50 are within 5 to 10 years, accounting for 78% of the total. Only about one-fifth of the standard age is more than 10 years, and most of these standards are basic common standards such as terminology, code, packaging, and particle size composition. The standard review and revision work is relatively timely, ensuring the timeliness of the standard.
51 international standards were adopted, 43 were transformed, 8 were not adopted because the international standards could not meet the market demand or the domestic experimental conditions were immature. The adoption rate was 84.3%, and the overall standard was better. Foreign advanced standards are used as reference for technical data and are not directly adopted.
1. The standard technology level is not high: there are many standards for medium and low-end products, and the standards embodying new technologies, new products and new methods are relatively lacking. Standards lag behind the development of the industry.
2, some standards can not meet the market demand very well: some products develop faster, standards are not revised in time, resulting in the standard technical content and market demand is out of line, can not effectively regulate the market and guide production.
3. Insufficient independent innovation: The data and technical indicators in some standards are directly or indirectly derived from domestic old standards or international and foreign standards, lacking scientific and effective experimental verification and technical research support, and even a few standards have been revised several times. The technical content is almost unchanged.
4. Insufficient safety standards: At present, there is only one mandatory standard, “General Abrasives Safety Rulesâ€. Superhard abrasives and coated abrasives only stipulate the rotation strength in some product standards, and the operability of some clauses. Not strong and the detection method is relatively backward.
5. Substantial participation in international standardization is not high: There is currently no international standard set by China.
4. Current projects
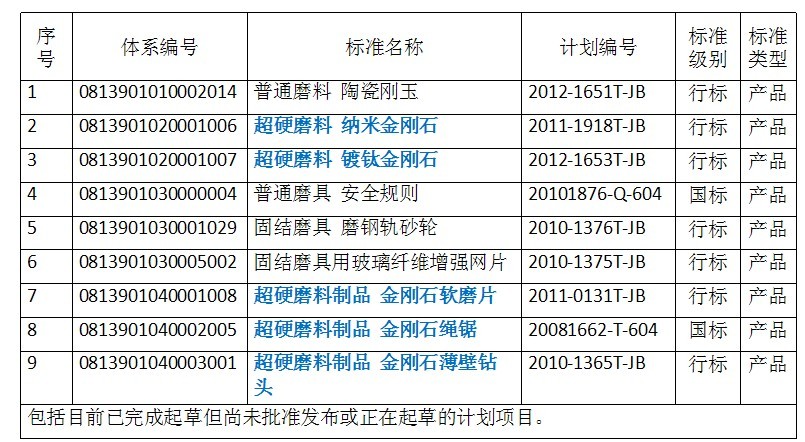
Development of standardization work in superhard materials and products industry
1 Basic situation of standard system for superabrasives and products
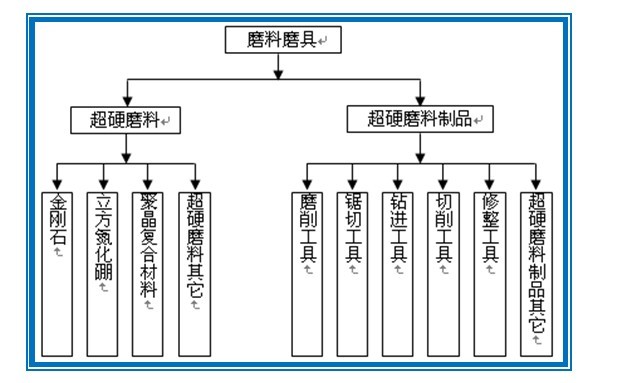
1.1 System Block Diagram
1.2 Existing structure of the system
Current standard catalog
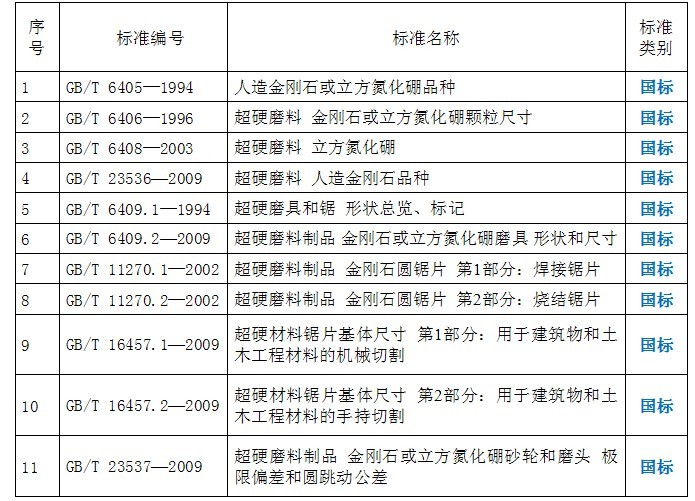
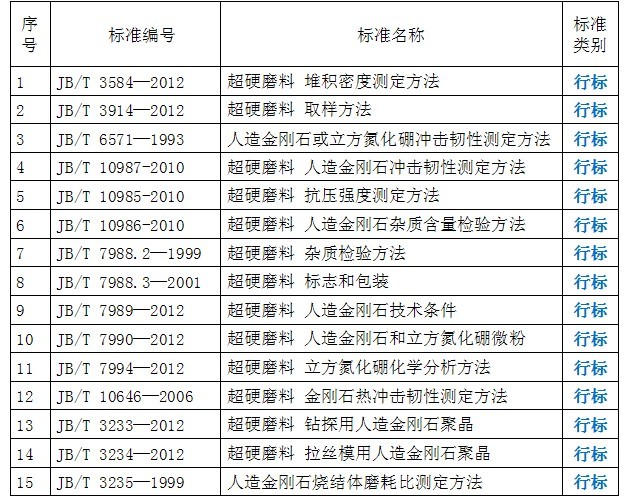

2 Superhard abrasives and product standardization features
2.1 Excellent conditions and wide space
Superhard abrasives and products are strategic emerging industries with high technological content, good development prospects and strong policy support.
2.2 Industry is developing rapidly and technology is changing with each passing day
New products, new technologies, and new methods have emerged in an endless stream, and even expanded to non-traditional fields other than grinding. The intersection and integration with other disciplines has become more and more in-depth.
2.3 Contradictions
The contradiction between the relatively backward standardization mechanism and the lagging standard technical content and the increasing market standardization demand - the main contradiction.
Although a relatively complete standard system has been basically formed at present, with the continuous emergence of new products, new technologies and new methods, the standardization work is far from meeting the market demand.
Standardization of superhard materials and products industry
3 Current projects
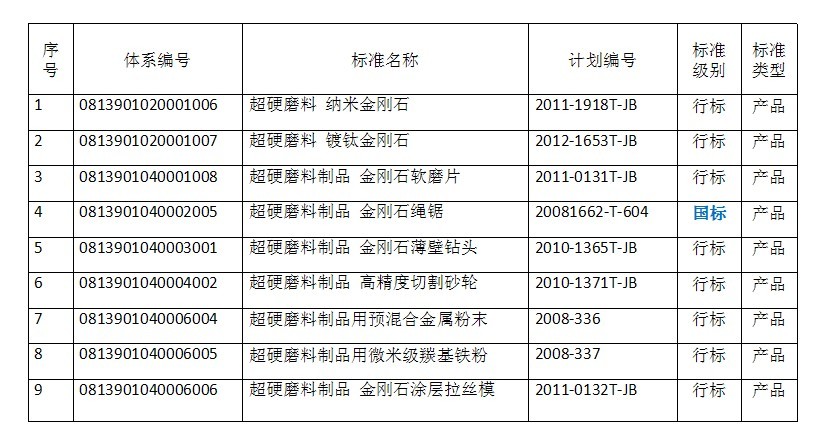
4 International Standardization Work Outlook
Among the 51 international standards in the field of sufficient abrasive abrasives, there are only 6 superhard abrasives and products, accounting for less than 12%, far behind the fixed abrasives (37.3%) and coated abrasives ( 27.5%) left plenty of room for our substantive participation in international standardization activities.
None of the big and not strong international standards was drafted by China, which is not commensurate with the status of our abrasive abrasives.
Although it is not related to the participation of our international standardization work, the deep reason is that China's abrasives industry is big but not strong.
The field of superabrasives and products has basically the conditions and strength for substantive participation in the formulation of international standards.
Standardization of superhard materials and products industry
Actions and goals:
Action 2011, delegation to participate in the 37th International Conference abrasive abrasive standard, which is China abrasives industry intervals for the first time to attend the meeting after more than two decades, it has aroused great attention of international organizations and national participants for China’s substantive participation in international standardization activities has played a positive role.
On June 5, 2013, the 38th International Abrasives Standards Meeting will be held, and will continue to participate in this meeting. It is expected to expand the depth and breadth of China's abrasives industry to participate in ISO activities, and strive for the right to speak internationally as soon as possible. Gain experience.
The goal is to take the opportunity of participating in the international standard meeting, aiming at submitting the international standard proposal as soon as possible, aiming at formulating the international standards led by China, and fully participating in the international standardization work, striving for the super hard abrasive at the end of the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" Substantial breakthroughs were made in the international standardization of products.
How to declare a standard plan project
1 Standard plan project reporting procedure
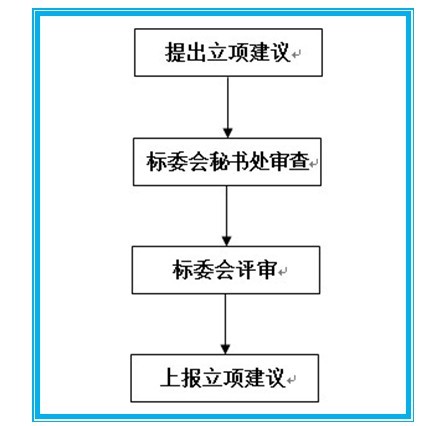
2 Procedures and requirements for proposing proposals
2.1 Procedures for proposing proposals
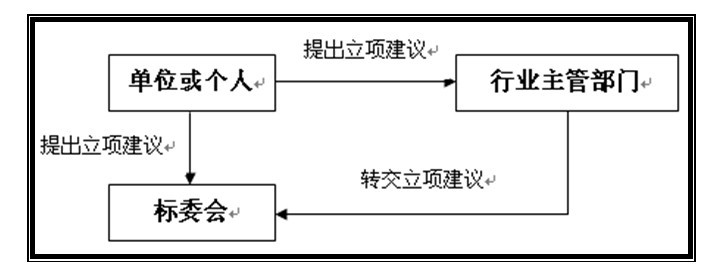
The standard revision plan project implements a perennial public collection system. Any unit or individual may, at any time, submit proposals to the National Professional Standardization Technical Committee or the Standardization Technical Focal Point according to the conditions for the standardization and revision of the planned project, or directly submit the project proposal to the relevant industry competent department (MCC). The competent department of industry (China Machine Tool Association) will forward the proposal submitted to the relevant standard committee.
The project proposal shall be accepted by the Standards Committee and submitted to the competent department of the industry (China Machinery Association) after review.
2.1.1 Basic requirements
(1) Comply with the current national laws and regulations and the relevant provisions of the standardization work (2) The scope and guiding principles of the project in line with national standards and industry standards (3) The urgent needs of the market and enterprises, in line with the national industrial development policy, to improve economic efficiency and society Benefits have a driving role. (4) The government urgently needs to promote the market order. (5) It is in line with the national adoption of international standards or foreign advanced standards. (6) It is conducive to the rational development and utilization of national resources and the promotion of scientific and technological achievements (7) Safeguarding safety and people's health, protecting the environment, and safeguarding the interests of consumers (8) Comply with the standard revision work plan in this field (9) Meet the requirements of the standard system in this field (10) Advanced technology, economical, safe and reliable (11) Coordinate with the existing standards, standards in the revision and revision (12) The main business scope of the responsible unit (13) The completion period of the national standard does not exceed three years, and the completion period of the industry standard does not exceed two years.
2.2 Requirements for project proposal
2.2.2 Qualification requirements
(1) The responsible unit of the standard project shall be a unit with certain technical strength and influence within the industry.
(2) The product standard project responsible unit should first consider the relatively advanced technology, relatively complete product specifications, professional standardization technicians, and medium-sized production units in similar enterprises.
(3) Method Standards The responsible unit of the project should first consider the units with test conditions related to the standard content, those with testing technology development capabilities, and those with professional testing techniques.
(4) Basic standards and safety standards The responsible unit of the project should first consider the comprehensive research institutes, national testing institutions, national industry centers, universities with higher research level, laboratories with provincial or higher level, or testing. Large enterprise in the center.
2.2.3 Material requirements
The unit or individual that proposes the proposal for the standard revision plan project shall submit the project proposal materials as required:
(1) A list of proposed materials for the project;
(2) A description of the proposed project;
(3) Standard project proposal;
(4) Draft standards;
(5) Description of the draft standard.
The unit or individual proposing the project proposal shall, when submitting the project proposal materials, provide the qualification certificate of the project responsible unit and the project personnel who are expected to undertake the standard system revision and drafting work, and explain in the “Description of the declared projectâ€.
Unit qualification certificate:
Unit nature, main business, technical strength, industry scale, status in the industry, etc.;
It is proposed to undertake the qualification certificate of the project personnel, the highest academic qualifications and technical titles, the situation of undertaking various standard revision work, the situation of obtaining scientific and technological achievements, and the situation of inventions, works and academic papers.
The unit that proposes the project proposal is not necessarily the responsible unit.
3 Procedures and requirements for review of proposed projects
3.1 Procedures for reviewing proposals
The review of the project proposal is the responsibility of the Secretariat of the Standards Committee. The Secretariat of the Standards Committee will review the form, content and qualifications of the submitted proposal materials, and after extensive consultation and coordination, decide whether to pass the review.
In principle, the proposal submitted before the end of June will be reviewed in the current year; the proposal submitted after the end of June will be reviewed in the following year.
3.2 Requirements for review of project proposals
3.2.1 Formal review
The Secretariat conducts a formal review of the integrity and normative nature of the material.
For the project proposal that the material does not meet the formal review requirements, the unit or individual who submitted the proposal shall be added or modified in writing until it meets the requirements.
How to declare a standard plan project
3.2.2 Content review
For the proposal to adopt the formal review, the Secretariat conducts a content review of the proposed materials.
For the proposal that the content does not meet the requirements, the unit or individual who submitted the proposal shall be added or modified in writing. The proposed amendments to the unqualified project will not be submitted to the review committee for review.
How to declare a standard plan project
3.2.3 Qualification review
For the project proposal that the form and content are in line with the requirements, the Secretariat will review the project-recommended units proposed by the project proposal and the qualifications of the project personnel to be undertaken.
For the project proposal that does not have the qualification of the responsible unit, the secretariat is responsible for conducting research on the relevant units in the industry, and gives suggestions for the project responsible unit according to the research situation.
How to declare a standard plan project
3.2.4 Request for comments
Through the proposal for review by the Secretariat, comments were sent in the form of a letter.
The Secretariat summarized the feedback. A proposal without objection is considered to have passed the review.
Objections with objections, coordination by the Secretariat, and conclusions on whether to pass the review based on coordination.
4 Procedures and requirements for review of project proposals
4.1 Procedure for reviewing proposals
After the project proposal is approved, the secretariat of the standard committee shall submit the standard committee or the corresponding sub-technical committee for review. The review can be conducted by means of a meeting review or a letter of review.
In principle, the proposal submitted before the end of June will be reviewed in the current year; for the proposal submitted after the end of June, it will be reviewed in the following year.
4.2 Requirements for review of project proposals
The Standardization Committee or the corresponding sub-technical committee shall make a feasibility study on the submitted project proposal in accordance with the principle and content requirements of the project, and conduct a qualification review for the project responsible unit, and make a consensus by the committee or the corresponding sub-committee of the technical committee. Submit a proposal for the project, suspend the report proposal, and fail to report the proposal.
For the project that the standard committee or the sub-technical committee makes a proposal to suspend the report, if there is any objection to the project responsible unit and there is no objection to the standard project content, the secretariat of the standard committee will be responsible for coordination, and after the meeting, Within a month, the coordination will be reported to the Standards Committee or the corresponding sub-committee of the technical committee, and the deputy director and the deputy director of the corresponding sub-committee shall make the decision of the project responsible unit and whether to submit the proposal.
For the project that the Standardization Committee or the Sub-Technical Committee makes a proposal to suspend the report, if there is any objection to the content of the standard project and there is no objection to the responsible unit of the project, the unit or individual proposes to rectify the problem raised by the review. And within one month after the meeting, the rectification materials will be reported to the Secretariat of the Standards Committee. The Secretariat of the Standardization Committee will propose whether to report the problem according to the rectification of the problem, and whether the standard committee or the corresponding sub-committee of the sub-committee will report the project. Suggested decision.
5 Procedures and requirements for reporting proposals
For projects that have passed the review by the Standards Committee or sub-technical committees, the Secretariat of the Standardization Committee is responsible for the unified organization, and regularly submits it to the higher-level standardization authorities for approval.
Activated Carbon
Activated Carbon is a black powder or block, granular, honeycomb amorphous carbon, but also a regular arrangement of crystalline carbon. In addition to carbon, activated carbon also contains two types of admixtures: one is a chemically bound element, mainly oxygen and hydrogen, which are left in the charcoal due to incomplete carbonization, or are foreign in the activation process. Non-carbon elements are chemically bonded to the surface of activated carbon; another type of admixture is ash, which is the inorganic part of activated carbon, and ash can easily cause secondary pollution in activated carbon. Activated carbon is widely used in production and life due to its strong adsorption.
Activated Carbon
Activated Carbon,Coal-Based Activated Carbon,Granular Activated Carbon,Wood Based Activated Carbon
Hwa Seng Resources (Hong Kong) Co., Limited , http://www.hwaseng-resources.com
