Microbial electrosynthesis (Microbial electrosynthesis) is a process in which microorganisms use electrical energy as reducing power to reduce CO2, glucose or other substrates into various chemicals. . Cathode electrons are converted into reducing equivalents in the cell, which provides reducing power for the fixation of intracellular CO2 and the reduction of fumaric acid to succinic acid. As the greenhouse gas emission problem becomes more and more serious, microbial electrosynthesis technology, as a green and sustainable bio-carbon fixation technology, has become a hot research topic today.
Recently, the microbial metabolic engineering research team led by researcher Zhang Xueli of the Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the metabolic engineering and synthetic biotechnology research team led by researcher Bi Changhao have made important progress in microbial electrosynthesis technology. The Research Park focuses on the influence of the intracellular coenzyme system on the electrical activity of cells. Based on the previously constructed E. coli electrosynthesis fermentation system, the intracellular synthesis of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) was modified to improve the intracellular The level of FAD, thereby increasing the electrical activity of E. coli. The study also found that the microbial electrosynthesis system is conducive to the synthesis of reducing products (lactic acid, ethanol, etc.), and the efficient synthesis module of succinic acid is assembled into the electrical cells of E. coli with high electrical activity, and the conversion rate of succinic acid is greatly improved. This study provides new ideas for further enhancing the performance of E. coli electrical energy cells.
The research was supported by the key deployment project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, "CO2 Artificial Bioconversion". Related results were published in Biochemical Engineering Journal. Wu Zaiqiang, a doctoral student jointly trained by Tianjin Institute of Technology and Engineering and Nanjing University of Science and Technology, is the first author of the paper, and Bi Changhao and Zhang Xueli are the corresponding authors.
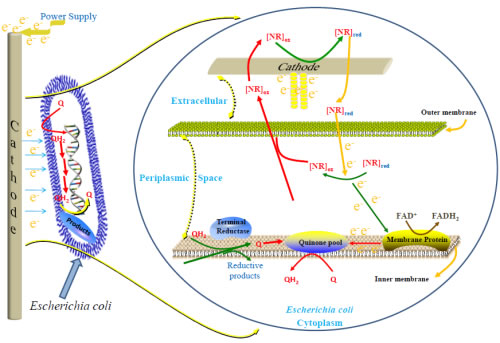
Possible connection between cellular FAD level and electrical activity
Non-contact Body Infrared Thermometer

Oral Glass Thermometer,Glass Thermometer,Digital Thermometer ,Infrared Thermometer
Dongguan Maimeng Culture and Creative Co. Ltd , https://www.factorydirectmask.com
